Tuesday, November 3, 2009
How To Create An Access Database Parameter Query in Video
src="http://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/show_ads.js">
Tuesday, June 30, 2009
What are the most popular applications are using MS Access?
Some are built by programmers of small to medium scale businesses. However, some large enterprises also use MS Access for their enterprise wide applications, testifying to the power and flexibility and security features of this software.
Why dont you try exploring the features and power of MS Access to build your own applications? Now is the time to reap the benefits this powerful database software that is readily available in most personal computers running MS Windows and MS Office applications.
Wednesday, April 29, 2009
Linking to an Oracle 10G database through ODBC
2. Right click on the center of your MS Access work area and click the "Link Tables" as shown.

3. The Link dialog box would appear as shown below.

4. Click the "Files of Type" pull down menu and click "ODBC Databases".

5. The "Select Data Source" dialog box appears. Click the "New" button.

6. The "Create New Data Source" dialog box opens. The Oracle 10G datasource is already in the dialog if you have already installed it. If you have not yet installed it, download the Oracle 10G ODBC driver from the internet and install in your computer. Click the Oracle 10G driver from among the choices.

7. Type the name you want for your datasource as in shown below. You can name it according to your preferred name, then click "Next".

8. Click the "Finish" button as shown below.

9. Type the credentials required for the database you are connecting/linking to. Service Name (usually "localhost"), user name and; password. Click the "Ok" button.
Sunday, April 12, 2009
MS Access as an Audit Tool part 2!
1. Connecting to another database through an ODBC driver.
2. Converting data extracted by the I.T. unit into an MS Access tables.
In this post, I will explain to the reader how to connect to another data source like Oracle, MySql and others through an ODBC driver.
Knowledge on how to do this is vital if your Audit organization does not have the budget to buy expensive audit tools like ACL or IDEA that would serve as their CAATs software. If you could train your auditors who have an inclination with the workings of database softwares, you could very well create audit tools that are as powerful as ACL or IDEA and easily customizable according to your needs.
ODBC stands for Open Database Connectivity
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is Microsoft's strategic interface for accessing data in a heterogeneous environment of relational and non- relational database management systems. Based on the Call Level Interface specification of the SQL Access Group, ODBC provides an open, vendor- neutral way of accessing data stored in a variety of proprietary personal computer, minicomputer, and mainframe databases. ODBC alleviates the need for independent software vendors and corporate developers to learn multiple application programming interfaces. ODBC now provides a universal data access interface. With ODBC, application developers can allow an application to concurrently access, view, and modify data from multiple, diverse databases. - Microsoft Help and Support, Article ID: 110093 - Last Review: March 29, 2007 - Revision: 1.5
ODBC--Open Database Connectivity Overview.
In order to connect to another data source or database, you need an ODBC client and an ODBC driver. The client is the Microsoft Access since it is an ODBC enabled front-end and the one which the user sees on the screen. While your ODBC driver is the one that handles the communication between your client or front end and another database. Microsoft Access has a couple of ODBC drivers already built in its system. However, if MS Access is not pre-loaded with the ODBC driver you require, you may download it from the internet where most ODBC drivers are readily available for download, you may do so and install it in your system.
For example if your back end database is Oracle 10G, download the ODBC driver for the Oracle 10G database from the Oracle website and install the driver in your operating system. Be sure to download the version applicable to your operating system.
--- See next blog post for an example of connecting to an Oracle 10G database from MS Access ---
Saturday, March 21, 2009
Flash MS Access Tutorials!
How to create a new MS Access 2003 database
How to open an MS Access 2003 database
How to load MS Access 2003 database
Thursday, March 19, 2009
Using MS Access Queries to retrieve and display data
a.1 SELECT statement
Selecting All Columns
SQL script: Type the sql script in the SQL view of a query as in the
lines below.
Select * from tablename
--- or ---
Go to query design view as shown below.
Microsoft Access Design View:
1. Drag the asterisk of the selected table in the table or query area to
the design grid. Click Run button or View button.
See picture below.
Selecting Columns and Changing Column sequence
SQL script: Type the sql script in the SQL view of a query.
Select columname, columname, columname from tablename
Microsoft Access Design View:
1. Drag the column names of the selected table in the table or query area to the design grid according to your preferred sequence. Click Run button or View button.
Manipulating Column Names
Select columname as name, columname as name from tablename
In design view:
Change the name of the column by typing the preffered name before the column name as in the example: Accountnumber: acct_no
Accountnumber is the preffered name
acct_no is the fieldname or column name in the database
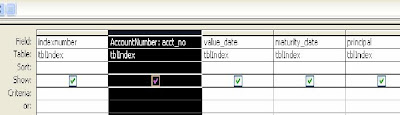
a.
Tuesday, March 17, 2009
Create an MS Access table from scratch
Text
Use for text or combinations of text and numbers, such as addresses, or for numbers that do not require calculations, such as phone numbers, part numbers, or postal codes.
Stores up to 255 characters. The FieldSize property controls the maximum number of characters that can be entered.
Memo
Use for lengthy text and numbers, such as notes or descriptions.
Stores up to 63,999 characters.
Use for data to be included in mathematical calculations, except calculations involving money (use Currency type).
Stores 1, 2, 4, or 8 bytes; stores 16 bytes for Replication ID (GUID). The FieldSize property defines the specific Number type.
Date/Time
Use for dates and times. Stores 8 bytes.
Currency
Use for currency values and to prevent rounding off during calculations. Stores 8 bytes.
AutoNumber
Use for unique sequential (incrementing by 1) or random numbers that are automatically inserted when a record is added. Stores 4 bytes; stores 16 bytes for Replication ID (GUID).
Yes/No
Use for data that can be only one of two possible values, such as Yes/No, True/False, On/Off. Null values are not allowed. Stores 1 bit.
OLE Object
Use for OLE objects (such as Microsoft Word documents, Microsoft Excel spreadsheets, pictures, sounds, or other binary data) that were created in other programs using the OLE protocol. Stores up to 1 gigabyte (limited by disk space).
Hyperlink
Use for hyperlinks. A hyperlink can be a UNC path or a URL.
Stores up to 2048 characters.
Lookup Wizard
Use to create a field that allows you to choose a value from another table or from a list of values using a combo box—-choosing this option in the data type list starts a wizard to define this for you.
Requires the same storage size as the Primary Key that corresponds to the Lookup field ---- typically 4 bytes.
Steps in Creating a Table in Design View
1.Click the table tab in the Groups menu bar.
2.Click “New” in the Toolbar pane to load the New Table dialog box.
3.The New Table dialog box choices are the following: Datasheet View, Design View, Table Wizard, Import Table and Link Table.
4.Choose “Design View” and click “OK”.
5.In the Design View, the user specify the field name and data type of the field.
Exercise in creating a table:
Table Name: DisbVoucher
Fields/Attributes:
DVNumber (number, primary key, length=user defined)
PayeeName (text, length = 60)
Particulars (memo)
Table Name: DVDetails
Fields/Attributes:
DVEntryID (number, primary key, length=user defined)
DVNumber (Lookup to DVNumber field of DisbVoucher table)
Debit (currency, decimal=2, format=standard)
Credit (currency, decimal=2, format=standard)
Linking your tables or creating relationships
Lookup Wizard – creates a field limited to a list of values based on other fields from other tables or you can type the valid values.
Using the Lookup Wizard:
1. Choose the Lookup Wizard from the data type choices.
2. Choose to Lookup from other tables or queries or choose to type the valid values.
3. If you choose to Lookup from other tables or queries, choose from among available queries or tables presented by Access.
Using the Relationships Window
1. Click the Tables tab in the Group menu bar.
2. Click “Relationships” to load the table relationships which looks like the one one shown below.

Saturday, March 14, 2009
Microsoft Access 2003 part 3
A way of locating/retrieving information in an Access database in order for a user to view, change/update or analyze. A query is also a question, answer to such is retrieve from the database. Query results can be the basis for other access objects like another query or reports.
SQL view – you can create a query in this view by typing the query using an SQL (Structured Query Language) syntax.
Design view – you can create a query in this view by dragging the chosen field of a particular table or another query from the table area to design grid.
Types of Queries
Select query – the most common type of query. Created by selecting information from chosen tables (based on user criteria). Information is displayed in datasheet for viewing and analysis. Changes can be made to the underlying data, the user should be careful not to make accidental changes.
Update query – a query that updates/modify data in the underlying table.
Append query – a query that appends data to the underlying table.
Delete query – a query that deletes records from the underlying table based on a criteria set by the user.
Crosstab query – a special type of query that summarizes data based on user defined row headings and column headings.
Forms
A window or user interface where you can place controls for users to view or enter information.
Form view – the view in which you enter data.
Design view – you work with the controls and properties of the form to refine how its works and looks.
Datasheet view – looks like a table in opened in datasheet view.
Reports
Display information based on tables or queries in a format chosen by the user. Report objects can be programmed to respond to user choices. Can include information from multiple tables and queries, calculated values from database information, elements that can be formatted such as headers, footers, titles, and headings.
Design view – where you can make changes to report design as in the case of form design view.
Print preview – show exactly how a report looks when printed.
Layout preview – the same as print preview except that not all details are shown.
Macros
Used by Access to respond to an event. Macros can be executed using a VBA (visual basic for application) code through form buttons that are clicked by users. Macros automate common routines like opening and closing forms or printing of reports.
Modules
VBA programs that are more powerful than macros. VBA is a high level programming language present in every MS Office application. If you have programmed before with Visual Basic, the VBA environment and syntax would be familiar to you. VBA has hundreds of commands that can handle complex operations that cannot be handled by macros.
Thursday, March 12, 2009
Microsoft Access as an Audit or Analysis Tool!
1. Provide your MS Access database with read only connection to your corporate databases. This can be accomplished by downloading an "Open Database Connectivitiy (odbc)" driver. The odbc driver must be specific to the type and version of your corporate database system. Ex. If your company utilizes Oracle 10g, then you must download Oracle 10g odbc driver. Ask assistance from you I.T. unit in connecting your MS Access after you have installed the driver in your PC unit, or seek assistance in installing the odbc driver if you are not allowed to install such drivers without their consent.
2. If you are not allowed to connect to your corporate database, then request for an extraction of your needed data for a specific period depending upon your need. You may request data in dbase format, foxpro format, textile or other specific format. However, most I.T. units would provide you with text file formats because this is the most safe format to convert data to in order to avoid extraction errors.
----- More on my next post on the field formats you should require on your textfile conversions from your I.T. unit and how you convert the text files into MS Access tables --------
Monday, March 9, 2009
Microsoft Access 2003 part 2
The Database Window has three (3) basic parts:
- Objects menu bar and Groups menu bar
- Toolbar
- Open pane
The image below shows the database window and its 3 parts.
The Objects Menu bar is composed of seven (7) tabs: Tables, Queries, Forms, Reports, Pages, Macros and; Modules.
Tables
The main object in any database, the purpose of which is to store information. A database object has two or more views, and tables has two views, namely design view and datasheet view.
Datasheet view – you can view and modify the table data.
Design view – you can view and modify the table structure.
Datasheet View of a table
Design View of a table

Saturday, March 7, 2009
Microsoft Access 2003 part 1
- Microsoft Access is part of the MS Office suite, the latest version of which is MS Office 2007 to which Access 2007 is a part of.
- The initial screen and look and feel of the new MS Office 2007 is very much different from the 2003 version, the basic functionality however is still the same. This is usually the case with new Microsoft versions of its products, they just change the look and feel but not the core functionality of the software.
- Access can convert from and to other database or file formats:
Ex. Excel, textfile, foxpro, dbase, oracle, mysql and etc.
Opening, Creating and Closing an Access Database:
Opening Microsoft Access
- From the Start menu, you select Start, Programs, Microsoft Office Microsoft Office Access 2003 ; or
- From the Start menu, you select Start, Programs, Microsoft Office Access 2003; or
- If the MS Access icon is in the desktop, just click on the icon.
Creating a new Microsoft Access database
- If the task pane is open click New, Blank Database, or if the task is not open, click the File Menu and click New, the task pane will now be open and you can click Blank Database.
Opening an Existing Microsoft Access Database
- If MS Access is already open, click the Open button or icon in the toolbar, and navigate to where your access database file is located in your harddisk; or
- Navigate to where your access database file is located and double click your existing access database file.
Closing a Microsoft Access database
- Click the File menu then click Close; or
Click the close symbol “X” on uppermost part of the database window, or just close Microsoft Access.
Sunday, March 1, 2009
Microsoft Access as an Audit Tool!
MS Access is a full featured database software that is both powerful and easy to learn and use. It can be utilized by accountants and auditors to assist them in their work.
My initial curiosity about the workings of MS Access started in 1997 while working for Sharp (Phils.) Corporation. I purchased a book about Access in order to learn the functionality of this program. I soon discovered the power of its query and report capability. I used it to convert Dbase files into MS Access tables and begin to improve my skills creating queries and reports. Instead of printing the Dbase files and manually calculating discounts to give to dealers based on their purchases from Sharp, I can now produce the information through MS Access queries in 30 minutes or less what usually took hours and days. In addition, reports can be prepared out of query results in a flash. More on how to utilize Access in my next blog post.






